When you apply a group policy on a container or OU, it applies to all users or computers in that container. However, you can exclude single or multiple users or containers from the policy applied. This tutorial shows you how to exclude a single user from a group policy object.
Exclude a user from group policy object in Windows Server
Step 1. Open server manager dashboard. Click Tools -> Group policy management
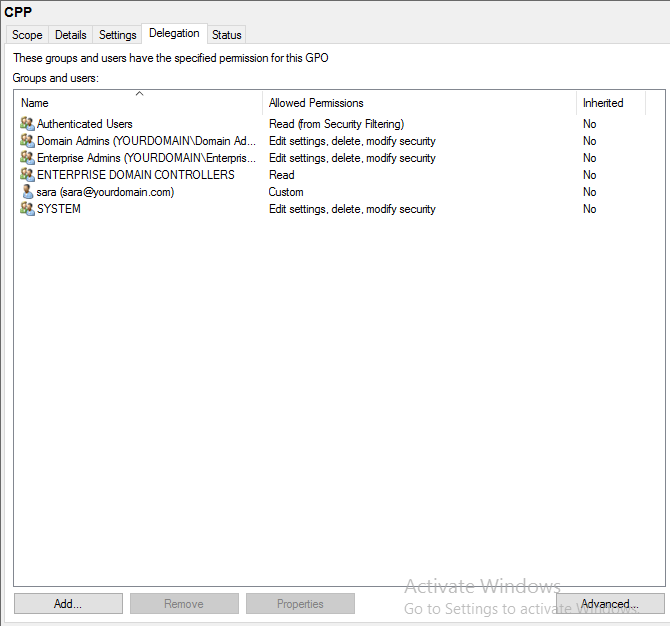
Step 2. In the group policy management editor, open the group policy object you want to apply an exception on (Located in Group Policy Objects).
Step 3. Click Delegation tab -> Advanced
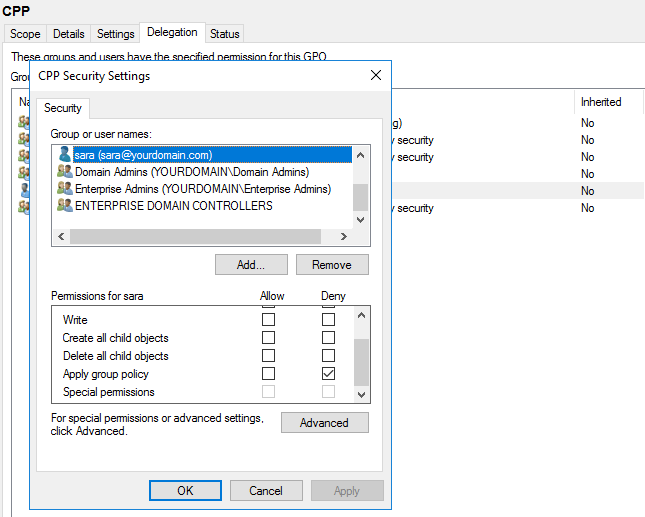
Step 4. Click Add and choose the user whom you want to exclude from group policy enforcement.
Step 5. Choose the user you entered in step 4.
Step 6. Locate Apply group policy in permissions and checkmark deny.
Step 7. Click Apply and then OK.
Step 8. Link the group policy to a container or OU (If you haven't done already).
Step 9. Execute the command:
gpupdate
on the command prompt.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Group Policy Object (GPO) in Windows Server?
A Group Policy Object (GPO) is a feature in Windows Server that allows network administrators to manage and configure operating system, user, and application settings across computers and users within an Active Directory environment.
Can I exclude a specific user or computer from a GPO?
Yes, you can exclude a specific user or computer from a GPO. This is often necessary for troubleshooting, applying specific policies to certain users or computers, or for overriding policies in special cases.
How do I exclude a user or computer from a GPO?
To exclude a user or computer, you need to use the "Security Filtering" or "Delegation" tab within the GPO Management Console. You can specifically deny the 'Apply Group Policy' permission for the user or computer you want to exclude.
What is Security Filtering in GPO?
Security Filtering is a feature in GPO that allows you to specify which users or computers a GPO applies to. Removing a user or computer from the security filtering section effectively excludes them from the GPO.
What steps are involved in excluding a user or computer using Security Filtering?
To exclude using Security Filtering:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- Find the GPO you want to modify.
- Select the "Scope" tab.
- In the "Security Filtering" section, remove the user or computer you want to exclude.
What is the Delegation tab method for excluding a user or computer?
The Delegation tab method involves specifically denying the 'Apply Group Policy' permission for the user or computer you want to exclude. It's a more direct approach compared to modifying security filtering.
How do I exclude a user or computer using the Delegation tab?
To exclude using the Delegation tab:
- Open GPMC and go to the desired GPO.
- Click on the "Delegation" tab.
- Click “Advanced,” find the user or computer, and set the 'Apply Group Policy' permission to 'Deny'.
Are there any risks associated with excluding a user or computer from a GPO?
Excluding users or computers from a GPO can lead to inconsistent policy applications across your network, which might result in security vulnerabilities or operational issues. It’s important to manage and document any exclusions carefully.
Can I exclude a group of users or computers?
Yes, you can exclude a group of users or computers by adding the entire group to the Security Filtering or Delegation sections and setting the appropriate permissions.
Will the changes take effect immediately after excluding a user or computer?
The changes may not take effect immediately. Users may need to log off and log back on, or computers may need to be restarted. You can also force a Group Policy update using the:
gpupdate /force
command.
Remember, managing GPOs requires understanding how Active Directory and Group Policies work. Incorrect settings can lead to network issues, so proceeding with caution is important.