The following command can be used to check and repair all MySQL databases on a Ubuntu or Debian Linux System. I've tested the commands on Ubuntu 20.04 and Debian 10.
Repair MySQL databases on Ubuntu Linux
sudo mysqlcheck --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf --auto-repair --optimize --all-databases
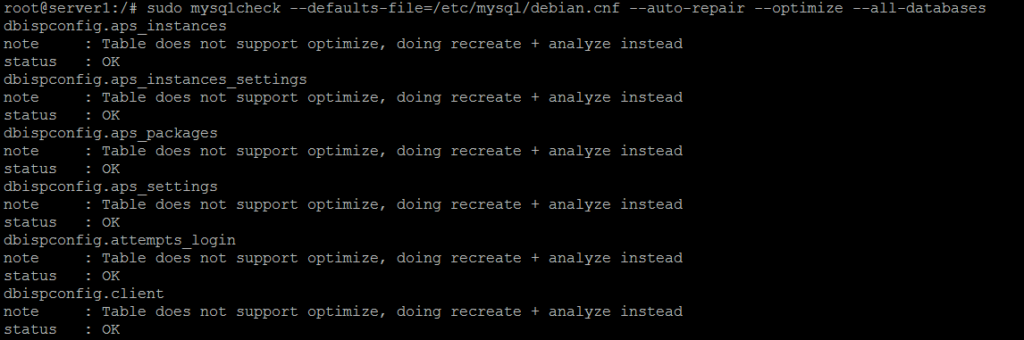
MySQL database repair on Debian
mysqlcheck --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf --auto-repair --optimize --all-databases
The benefit of the above command is that it uses the debian-sys-maint login to MySQL which is available on every Debian and Ubuntu System, so you don't have to provide the MySQL root login details.